Treatment Of Advanced Retinal Diseases
The eye is a complex system made up of many different layers and components, each with their part to play. The retina is a thin layer of tissue that covers the inside of the back of the eye, and its purpose is to receive light from the eye lens and convert it into signals that are then sent to the brain for processing. A healthy retina is vital for good vision, but there are a variety of issues that can occur in this specific region of the eye.
They can be treated with medication, laser or surgery. Quirónsalud has some of the best retina specialists in Dubai and we strive to provide you with exceptional eye care. Some of the problems affecting the retina that are treated with laser are retinal tears, diabetic retinopathy, and retinal vein occlusion. Surgical treatment is based on two techniques: scleral surgery and vitrectomy. The former is used only occasionally, and vitrectomy is useful for retinal detachment, vitreous haemorrhage, or macular holes. It consists of the removal of the vitreous gel, allowing access to the retina to treat it.
Retinal Detachment Requires Surgery Within
24 Hours
The Success Rate Of Diabetic Retinopathy Treatment Is
90%
if applied on time
Retinal Medical Conditions
Diabetic Eye Disease (Diabetic retinopathy)
Diabetes mainly causes two types of damage to the retina. In the 1st type of damage, leakage occurs from small blood vessels causing swelling which, if it occurs in the center of vision, can blur vision. Laser can be used in some individuals to stop this leakage. In the 2nd type of damage, existing blood vessels are blocked, and new blood vessels grow into the eye where they can break and bleed. Laser treatment is used to stop these blood vessels from growing and reducing the risk of vision loss.
Retinal Vein Occlusion
A retinal vein occlusion occurs when one of the miniscule veins in the retina is blocked by a blood clot. High blood pressure and cholesterol levels, smoking and glaucoma can all be risk factors for this issue, which usually leads to a gradual decline in vision in the affected eye. Retinal vein occlusion is usually painless, and aside from the risk factors it is not known what causes it.
Aging Retinal Disease (Macular Degeneration)
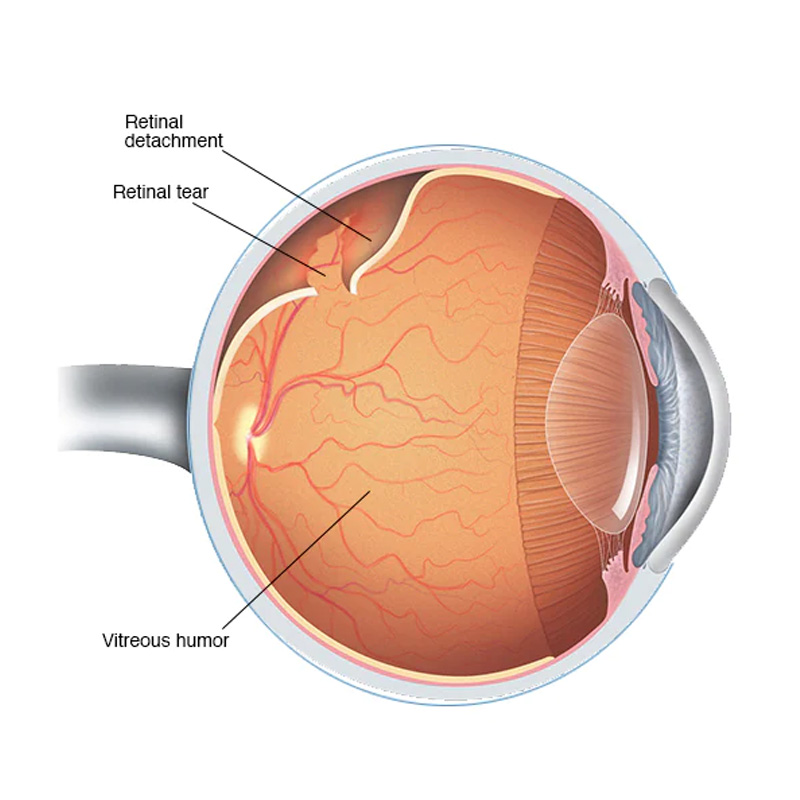
Retinal Tear
During a retinal tear, laser treatment seals the layers of the retina together. If not treated, fluid leaks through these tears or holes causing these layers to separate and detach. This causes loss of vision depending on the degree of detachment.
Advanced Retinal Diseases Treatment FAQs
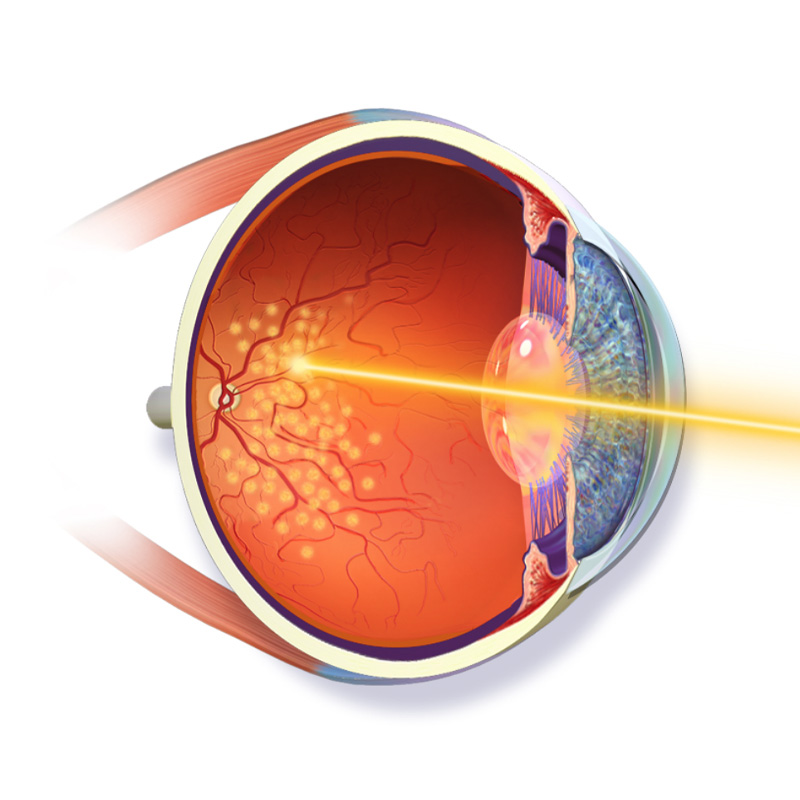
How Retina Laser Treatment Works
- Your pupils will be dilated to give your doctor a good view.
- You will be seated at a microscope, similar to the one used in your doctor’s office, as the laser beam is controlled through the microscope.
- Local anesthetic (freezing drops) will be placed in your eye. This is to prevent discomfort from the special contact lens placed on your eye to hold your lids apart. This lens also magnifies the area being treated.
- During treatment, you will see bright flashes of light. Laser treatment is almost always painless, although sometimes a patient may have slight discomfort.
After The Retina Laser Treatment
- Your vision will be blurred immediately after your treatment, due to the dilation drops. This will clear in 3 – 4 hours.
- Continue your usual eye drops and medications.
- Your doctor will instruct you about any activities that you should limit.
Diabetic Retinopathy Treatment
The first step to prevent Diabetic Retinopathy is to control the blood sugar and high blood pressure, change in food and nutrition patterns and change in lifestyle habits, mainly, more exercise. The most common treatment for diabetic retinopathy is laser photocoagulation, which has proven to reduce severe vision loss by as much as 90%. However, its effect is reduced in patients who already suffer from diminished sight. Thus, it is very important for the treatment to be provided on time. We also have medications that can be injected in the eye, to decrease inflammation or risk of bleeding.
The Retina Consultant will indicate the best moment to proceed with Laser Photocoagulation or Intravitreal Injections. In the most severe cases, we opt for surgery. The technique used for these interventions on the retina is called vitrectomy and consists of extracting the gel that fills the eye in order to reach the retina and treat it. At the same time, we remove the fibrous bands that pull on the retina and cause tractional detachment. The procedure is usually finished off with laser.
Retinal Detachment
Retinal detachment is a serious eye disease that consists of the separation of the retina from the eye wall. A detached retina causes loss of vision. Initial symptoms can be: sudden appearance of floaters, flashes or a dark curtain that obstructs the vision. It is important to point out that these symptoms do not always signify the presence of a retinal detachment, however, if you notice them, it is advisable to perform a dilated examination (the pupil is dilated with drops).
Risk factors are: myopia, areas of peripheral retinal thinning, a family history of retinal detachment, prior retinal detachment in the other eye, ocular trauma or a history of complicated eye surgery. If retinal detachment is not detected and treated within the first few days, vision loss may be permanent.
The treatment for retinal detachment is surgical, and consists of putting the retina back in its place using different techniques: scleral surgery, vitrectomy, or a combination of both.
Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD)
Age-related macular degeneration, or AMD, is a disease that causes macular deterioration in people over 60. The macula is the central part of the retina, where there are more photoreceptors and, thus, it is the part responsible for fine, detailed vision.
Advanced age is, without a doubt, one of the most significant risk factors, however, a family history of AMD, smoking, high cholesterol and blood pressure, and the sunlight are also responsible for this disease. There are two types of age-related macular degeneration: dry (atrophic) and wet (neovascular).
The dry type is the most common; it produces yellowish deposits on the macula (drusen) and atrophy areas. It progresses slowly and, in some cases, is asymptomatic (does not cause any discomfort). In some patients, there may be moderate vision loss, but only rarely can impose limits on the patient’s daily activities. Currently, there is no treatment for these patients, and doctors prescribe vitamin and antioxidant supplements to stop or slow the disease’s progression.
In the wet type, blood vessels, in the form of a fibrovascular membrane, invade the space below the retina, causing severe inflammation and vision loss which can take place in just a few days. It is important to know that this type of AMD can be treated, but the results depend on how quickly treatment begins. If the patient consults an ophthalmologist immediately, results are far better.
Nowadays, treatment consists of administrating a medication into the eye, using an injection, which allows us the maximum efficiency in treatment with no side effects. It is not painful. The full treatment consists of three monthly injections and, afterwards, they can be repeated depending on the response to the treatment, though in most cases the first three are enough.
Artery & Vein Occlusions
An occlusion of the Central Retinal Artery can cause a severe loss of sight, which is irreversible in many cases. It is an acute emergency with few chances of recovery of vision unless it is treated in the first couple of hours.
Retinal vein occlusion is the second most common retinal vascular pathology, after diabetes mellitus, and mostly appears in people over 60 years old. In many cases, there is a significant loss of vision in the affected eye. The most common treatment is intraocular injection and photocoagulation of the affected area using argon laser.
Macular Hole
Book An Appointment
Fill the form below or call/whatsApp +971 50 309 3131 to book an appointment.
Early treatment can prevent long-lasting consequences