Urinary Tract Infections
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is a common bacterial infection that affects any part of the urinary system, including the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. UTIs are more common in women than men and are usually caused by bacteria that enter the urethra and then travel up to the bladder or kidneys.
Symptoms of a UTI may include a strong, persistent urge to urinate or a burning sensation during urination. Our Urology Department at Quironsalud Dubai is experienced in managing the various infections and provide the best treatment options.
Risk Factors
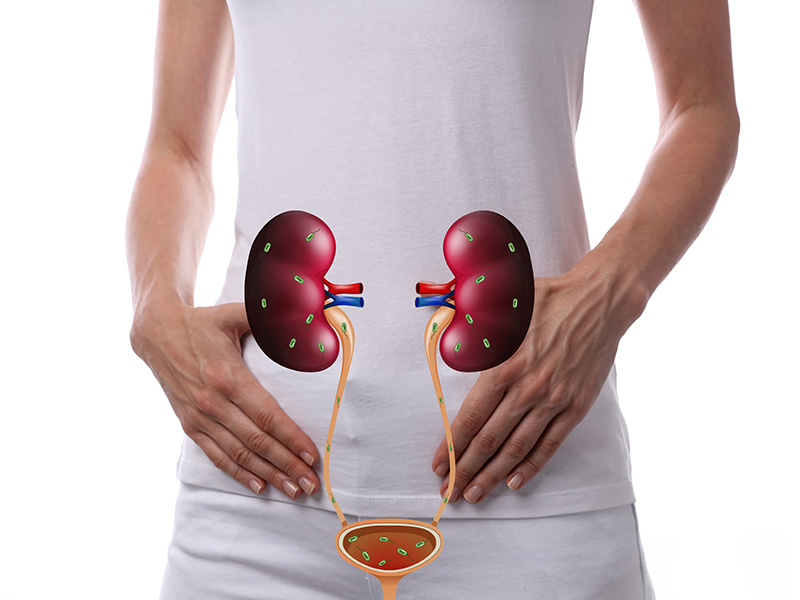
Several factors can increase the risk of developing a urinary tract infection (UTI). Some common risk factors for UTIs include:
- Gender: Women are more likely to develop UTIs than men, largely due to their shorter urethra, which makes it easier for bacteria to enter the urinary tract.
- Sexual activity: Sexual activity can introduce bacteria into the urinary tract and increase the risk of developing a UTI.
- Urinary tract abnormalities: Structural problems in the urinary tract, such as a kidney stone or an enlarged prostate, can increase the risk of UTIs.
- Urinary catheter use: Urinary catheters are tubes that are inserted into the bladder to drain urine and can increase the risk of bacterial infection.
- Diabetes: Diabetes can impair the immune system and increase the risk of UTIs.
- Weakened immune system: Certain medical conditions or medications that suppress the immune system can increase the risk of UTIs.
- Age: The risk of UTIs increases with age, as bladder and urinary tract function may decline.
- Family history: Individuals with a family history of UTIs may be more likely to develop them.
It is important to identify and address any underlying risk factors for UTIs to reduce the risk of developing these infections.
Signs & Symptoms
The signs and symptoms of a urinary tract infection (UTI) may vary depending on the affected part of the urinary system. However, some common signs and symptoms of UTIs include:
- A strong, persistent urge to urinate
- A burning sensation or pain during urination
- Passing frequent, small amounts of urine
- Cloudy, strong-smelling urine
- Blood in the urine
- Pelvic pain (groin pain), in women
- Rectal pain, in men
If the infection spreads to the kidneys, additional symptoms may include:
- Back pain, usually on one side
- Nausea and vomiting
- High fever and chills
It is important to seek medical attention promptly if you suspect you have a UTI, especially if you experience any of these additional symptoms, as untreated infections can lead to more serious complications, such as kidney damage.
Diagnosis of UTI
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is typically diagnosed through a combination of symptoms, physical examination, and laboratory tests. To diagnose a UTI, your healthcare provider may:
- Ask about your symptoms and medical history, including any past UTIs or related conditions
- Perform a physical exam to check for signs of infection, such as tenderness or pain in the lower abdomen or back
- Collect a urine sample to analyze in a laboratory for signs of infection, such as the presence of bacteria.
Additional tests may be ordered to rule out other conditions that may have similar symptoms to a UTI, such as a sexually transmitted infection or kidney stones. If you have recurrent UTIs or are at high risk for complications, our Urology Doctor may also recommend additional testing, such as an ultrasound.

What are the Treatment Options of UTI?
The treatment for a urinary tract infection (UTI) typically involves a course of antibiotics to eliminate the infection. In addition to antibiotics, your healthcare provider may also recommend:
- Drinking plenty of water to help flush out the bacteria
- Avoiding irritants such as caffeine, and spicy foods that can irritate the bladder and make symptoms worse
- Taking pain relievers.
- Applying heat to the lower abdomen or back to relieve pain and discomfort